|
1
|
Li X, Lu J, Zhao Y, Guo W. Identification and Characterization of Oxidative Stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Related Genes in Esophageal Cancer. J Cancer 2025; 16:2103-2123. [PMID: 40302812 PMCID: PMC12036101 DOI: 10.7150/jca.104376] [Citation(s) in RCA: 0] [Impact Index Per Article: 0] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Key Words] [Track Full Text] [Figures] [Journal Information] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 09/28/2024] [Accepted: 03/06/2025] [Indexed: 05/02/2025] Open
Abstract
Increasing evidence highlights the critical roles of oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in tumor initiation and progression. However, the specific functions of related genes in esophageal cancer (ESCA) remain poorly understood. To investigate the impact of oxidative and ER stress on ESCA, this study analyzed the TCGA and GEO databases to identify 12 oxidative stress- and ER stress-related differentially expressed genes (OERDEGs). Pathway analysis revealed significant enrichment in critical processes such as PRC2-mediated methylation, oxidative stress-induced senescence, and NOTCH signaling. A novel LASSO regression model was developed to link gene expression with clinical prognosis, and the model was validated through ROC and Cox regression analyses. Four OERDEGs (CDKN3, PINK1, SPP1, and TFRC) were identified as key biomarkers for ESCA prognosis. Notably, TFRC expression was significantly upregulated in ESCA cells under both oxidative and ER stress conditions, in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Functional assays confirmed that TFRC promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulating the HIF-1α and NOTCH1 signaling pathways. This study elucidates the complex interplay between oxidative/ER stress and ESCA progression and highlights the innovative application of bioinformatics to identify potential biomarkers for early diagnosis and therapeutic strategies. Targeting TFRC, in particular, may offer a novel approach to improving ESCA treatment and enhancing patient prognosis.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Xiaoxu Li
- Department of Radiation Oncology, the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
| | - Juntao Lu
- Laboratory of Pathology, Hebei Cancer Institute, the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
| | - Yan Zhao
- Department of Oncology, the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
| | - Wei Guo
- Laboratory of Pathology, Hebei Cancer Institute, the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
| |
Collapse
|
|
2
|
Hao S, Cai D, Gou S, Li Y, Liu L, Tang X, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Shen J, Wu X, Li M, Chen M, Li X, Sun Y, Gu L, Li W, Wang F, Cho CH, Xiao Z, Du F. Does each Component of Reactive Oxygen Species have a Dual Role in the Tumor Microenvironment? Curr Med Chem 2024; 31:4958-4986. [PMID: 37469162 PMCID: PMC11340293 DOI: 10.2174/0929867331666230719142202] [Citation(s) in RCA: 2] [Impact Index Per Article: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Key Words] [MESH Headings] [Track Full Text] [Journal Information] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 03/24/2023] [Revised: 05/14/2023] [Accepted: 06/02/2023] [Indexed: 07/21/2023]
Abstract
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are a class of highly reactive oxidizing molecules, including superoxide anion (O2 •-) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), among others. Moderate levels of ROS play a crucial role in regulating cellular signaling and maintaining cellular functions. However, abnormal ROS levels or persistent oxidative stress can lead to changes in the tumor microenvironment (TME) that favor cancer development. This review provides an overview of ROS generation, structure, and properties, as well as their effects on various components of the TME. Contrary to previous studies, our findings reveal a dual effect of ROS on different components of the TME, whereby ROS can either enhance or inhibit certain factors, ultimately leading to the promotion or suppression of the TME. For example, H2O2 has dual effects on immune cells and non-- cellular components within the TME, while O2 •- has dual effects on T cells and fibroblasts. Furthermore, each component demonstrates distinct mechanisms of action and ranges of influence. In the final section of the article, we summarize the current clinical applications of ROS in cancer treatment and identify certain limitations associated with existing therapeutic approaches. Therefore, this review aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of ROS, highlighting their dual effects on different components of the TME, and exploring the potential clinical applications that may pave the way for future treatment and prevention strategies.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Siyu Hao
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
| | - Dan Cai
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
- South Sichuan Institute of Translational Medicine, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Shuang Gou
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
| | - Yan Li
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Lin Liu
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
- South Sichuan Institute of Translational Medicine, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Xiaolong Tang
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
| | - Yu Chen
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
- South Sichuan Institute of Translational Medicine, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Yueshui Zhao
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
- South Sichuan Institute of Translational Medicine, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Jing Shen
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
- South Sichuan Institute of Translational Medicine, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Xu Wu
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
- South Sichuan Institute of Translational Medicine, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Mingxing Li
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
- South Sichuan Institute of Translational Medicine, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Meijuan Chen
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Xiaobing Li
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Yuhong Sun
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Li Gu
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Wanping Li
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Fang Wang
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Chi Hin Cho
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- School of Biomedical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China;
| | - Zhangang Xiao
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
- South Sichuan Institute of Translational Medicine, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Department of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| | - Fukuan Du
- Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
- Cell Therapy & Cell Drugs of Luzhou Key Laboratory, Sichuan Luzhou, 646000, China
- South Sichuan Institute of Translational Medicine, Sichuan Luzhou 646600, China
| |
Collapse
|
|
3
|
Liu J, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Zhao H, Chen X, Zhong L, Shang D. Oxidative stress and autophagy-mediated immune patterns and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in gastric cancer. Aging (Albany NY) 2023; 15:12513-12536. [PMID: 37950729 PMCID: PMC10683600 DOI: 10.18632/aging.205194] [Citation(s) in RCA: 0] [Impact Index Per Article: 0] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Key Words] [MESH Headings] [Track Full Text] [Journal Information] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 04/06/2023] [Accepted: 10/04/2023] [Indexed: 11/13/2023]
Abstract
Recent years have seen a sharp rise in the amount of research on the connection between oxidative stress, autophagy, and cancer cells. However, the significant functions of oxidative stress and autophagy-related genes (OARGs) in gastric cancer (GC) are yet to be investigated integrally. Therefore, it will be a new and promising concept to search for novel OARG-related biomarkers to predict the prognosis and treatment response of GC. First, we assessed changes in prognosis and tumor microenvironment (TME) characteristics across the various oxidative stress and autophagy-related modification patterns based on a detailed analysis of 17 OARGs with prognostic significance of 808 GC samples. We identified three distinct OARG alteration patterns which displayed unique biological characteristics and immune cell infiltration features. Using principal component analysis methods, the OARGscore was developed to evaluate the OARG modification patterns of certain tumors. The negative connection between OARGscore and immune cells was statistically significant. Increased survival, a higher incidence of mutations, and a better response to immunotherapy were all predicted to be related to patients' high-OARGscore. In addition, the candidate chemotherapeutic drugs were predicted using the oncoPredict program. The low-OARGscore group was predicted to benefit more from Ribociclib, Alisertib, Niraparib, Epirubicin, Olaparib, and Axitinib, while patients in the high-OARGscore group were predicted to benefit more from Afatinib, Oxaliplatin, Paclitaxel, 5-Fluorouracil, Dabrafenib and Lapatinib. Our findings offer a specific method for predicting a patient's prognosis and susceptibility to immunotherapy, as well as a promising insight of oxidative stress and autophagy in GC.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Jifeng Liu
- Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
| | - Biao Zhang
- Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
| | - Yunshu Zhang
- Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
| | - Huahui Zhao
- Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
| | - Xu Chen
- Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
| | - Lei Zhong
- Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
| | - Dong Shang
- Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
| |
Collapse
|
|
4
|
Ito M, Mimura K, Nakajima S, Okayama H, Saito K, Nakajima T, Kikuchi T, Onozawa H, Fujita S, Sakamoto W, Saito M, Momma T, Saze Z, Kono K. M2 tumor-associated macrophages resist to oxidative stress through heme oxygenase-1 in the colorectal cancer tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2023; 72:2233-2244. [PMID: 36869896 PMCID: PMC10992489 DOI: 10.1007/s00262-023-03406-6] [Citation(s) in RCA: 0] [Impact Index Per Article: 0] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Key Words] [MESH Headings] [Grants] [Track Full Text] [Journal Information] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 11/01/2022] [Accepted: 02/11/2023] [Indexed: 03/05/2023]
Abstract
M2 tumor-associated macrophages (M2-TAMs) promote cancer cell proliferation and metastasis in the TME. Our study aimed to elucidate the mechanism of increased frequency of M2-TAMs infiltration in the colorectal cancer (CRC)-TME, focusing on the resistance to oxidative stress through nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway. In this study, we evaluated the correlation between M2-TAM signature and mRNA expression of antioxidant related genes using public datasets, and the expression level of antioxidants in M2-TAMs by flow cytometry and the prevalence of M2-TAMs expressing antioxidants by immunofluorescence staining using surgically resected specimens of CRC (n = 34). Moreover, we generated M0 and M2 macrophages from peripheral blood monocytes and evaluated their resistance to oxidative stress using the in vitro viability assay. Analysis of GSE33113, GSE39582, and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) datasets indicated that mRNA expression of HMOX1 (heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)) was significantly positively correlated with M2-TAM signature (r = 0.5283, r = 0.5826, r = 0.5833, respectively). The expression level of both Nrf2 and HO-1 significantly increased in M2-TAMs compared to M1- and M1/M2-TAMs in the tumor margin, and the number of Nrf2+ or HO-1+M2-TAMs in the tumor stroma significantly increased more than those in the normal mucosa stroma. Finally, generated M2 macrophages expressing HO-1 significantly resisted to oxidative stress induced by H2O2 in comparison with generated M0 macrophages. Taken together, our results suggested that an increased frequency of M2-TAMs infiltration in the CRC-TME is related to Nrf2-HO-1 axis mediated resistance to oxidative stress.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Misato Ito
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Kosaku Mimura
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan.
- Department of Blood Transfusion and Transplantation Immunology, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan.
| | - Shotaro Nakajima
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Hirokazu Okayama
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Katsuharu Saito
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Takahiro Nakajima
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Tomohiro Kikuchi
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Hisashi Onozawa
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Shotaro Fujita
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Wataru Sakamoto
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Motonobu Saito
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Tomoyuki Momma
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Zenichiro Saze
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| | - Koji Kono
- Department of Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
| |
Collapse
|
|
5
|
Wang XY, Beeraka NM, Xue NN, Yu HM, Yang Y, Liu MX, Nikolenko VN, Liu JQ, Zhao D. Identification of a three-gene prognostic signature for radioresistant esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Clin Oncol 2023; 14:13-26. [PMID: 36699628 PMCID: PMC9850665 DOI: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i1.13] [Citation(s) in RCA: 3] [Impact Index Per Article: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Key Words] [Track Full Text] [Download PDF] [Journal Information] [Submit a Manuscript] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 07/25/2022] [Revised: 10/25/2022] [Accepted: 12/06/2022] [Indexed: 01/10/2023] Open
Abstract
BACKGROUND Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is causing a high mortality rate due to the lack of efficient early prognosis markers and suitable therapeutic regimens. The prognostic role of genes responsible for the acquisition of radioresistance in ESCC has not been fully elucidated.
AIM To establish a prognostic model by studying gene expression patterns pertinent to radioresistance in ESCC patients.
METHODS Datasets were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus and The Cancer Genome Atlas databases. The edgeR, a Bioconductor package, was used to analyze mRNA expression between different groups. We screened genes specifically responsible for radioresistance to estimate overall survival. Pearson correlation analysis was performed to confirm whether the expression of those genes correlated with each other. Genes contributing to radioresistance and overall survival were assessed by the multivariate Cox regression model through the calculation of βi and risk score using the following formula: 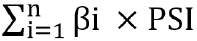 . .
RESULTS We identified three prognostic mRNAs (cathepsin S [CTSS], cluster of differentiation 180 [CD180], and SLP adapter and CSK-interacting membrane protein [SCIMP]) indicative of radioresistance. The expression of the three identified mRNAs was related to each other (r > 0.70 and P < 0.05). As to 1-year and 3-year overall survival prediction, the area under the time-dependent receiver operating characteristic curve of the signature consisting of the three mRNAs was 0.716 and 0.841, respectively. When stratifying patients based on the risk score derived from the signature, the high-risk group exhibited a higher death risk and shorter survival time than the low-risk group (P < 0.0001). Overall survival of the low-risk patients was significantly better than that of the high-risk patients (P = 0.018).
CONCLUSION We have developed a novel three-gene prognostic signature consisting of CTSS, CD180, and SCIMO for ESCC, which may facilitate the prediction of early prognosis of this malignancy.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Xiao-Yan Wang
- Department of Endocrinology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
| | - Narasimha M Beeraka
- Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
- Department of Human Anatomy, I. M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University, Moscow 119991, Russia
- Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, JSS College of Pharmacy, Mysuru 570015, India
| | - Nan-Nan Xue
- Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
| | - Hui-Ming Yu
- Department of Radiation Oncology, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing 065005, China
| | - Ya Yang
- Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
| | - Mao-Xing Liu
- Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education), Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery IV, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China
| | - Vladimir N Nikolenko
- Department of Human Anatomy, I. M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University, Moscow 119991, Russia
- M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow 119991, Russia
| | - Jun-Qi Liu
- Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
| | - Di Zhao
- Department of Endocrinology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
| |
Collapse
|
|
6
|
Liu W, Yang HS, Zheng SY, Luo HH, Feng YF, Lei YY. Oxidative stress genes in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: construction of a novel prognostic signature and characterization of tumor microenvironment infiltration. BMC Bioinformatics 2022; 23:406. [PMID: 36180848 PMCID: PMC9523924 DOI: 10.1186/s12859-022-04956-9] [Citation(s) in RCA: 4] [Impact Index Per Article: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Key Words] [Track Full Text] [Download PDF] [Figures] [Journal Information] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 03/19/2022] [Accepted: 09/21/2022] [Indexed: 11/22/2022] Open
Abstract
Background Oxidative stress plays an important role in the progression of various types of tumors. However, its role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) has seldom been explored. This study aimed to discover prognostic markers associated with oxidative stress in ESCC to improve the prediction of prognosis and help in the selection of effective immunotherapy for patients. Results A consensus cluster was constructed using 14 prognostic differentially expressed oxidative stress-related genes (DEOSGs) that were remarkably related to the prognosis of patients with ESCC. The infiltration levels of neutrophils, plasma cells, and activated mast cells, along with immune score, stromal score, and estimated score, were higher in cluster 1 than in cluster 2. A prognostic signature based on 10 prognostic DEOSGs was devised that could evaluate the prognosis of patients with ESCC. Calculated risk score proved to be an independent clinical prognostic factor in the training, testing, and entire sets. P53 signaling pathway was highly enriched in the high-risk group. The calculated risk score was positively related to the infiltration levels of resting mast cells, memory B cells, and activated natural killer (NK) cells and negatively associated with the infiltration levels of M1 and M2 macrophages. The relationship between clinical characteristics and risk score has not been certified. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values for sorafenib and gefitinib were lower for patients in the low-risk group. Conclusion Our prognostic signature based on 10 prognostic DEOSGs could predict the disease outcomes of patients with ESCC and had strong clinical value. Our study improves the understanding of oxidative stress in tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) and provides insights for developing improved and efficient immunotherapy strategies. Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12859-022-04956-9.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Wei Liu
- Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510080, Guangdong, China
| | - Hao-Shuai Yang
- Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510080, Guangdong, China
| | - Shao-Yi Zheng
- Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510080, Guangdong, China
| | - Hong-He Luo
- Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510080, Guangdong, China
| | - Yan-Fen Feng
- State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, 510060, Guangdong, China. .,Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, 510060, Guangdong, China.
| | - Yi-Yan Lei
- Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510080, Guangdong, China.
| |
Collapse
|
|
7
|
Yao J, Duan L, Huang X, Liu J, Fan X, Xiao Z, Yan R, Liu H, An G, Hu B, Ge Y. Development and Validation of a Prognostic Gene Signature Correlated With M2 Macrophage Infiltration in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front Oncol 2021; 11:769727. [PMID: 34926275 PMCID: PMC8677679 DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.769727] [Citation(s) in RCA: 21] [Impact Index Per Article: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Key Words] [Track Full Text] [Download PDF] [Figures] [Journal Information] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 09/02/2021] [Accepted: 11/16/2021] [Indexed: 12/24/2022] Open
Abstract
Background Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the most common type of esophageal cancer and the seventh most prevalent cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Tumor microenvironment (TME) has been confirmed to play an crucial role in ESCC progression, prognosis, and the response to immunotherapy. There is a need for predictive biomarkers of TME-related processes to better prognosticate ESCC outcomes. Aim To identify a novel gene signature linked with the TME to predict the prognosis of ESCC. Methods We calculated the immune/stromal scores of 95 ESCC samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) using the ESTIMATE algorithm, and identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between high and low immune/stromal score patients. The key prognostic genes were further analyzed by the intersection of protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks and univariate Cox regression analysis. Finally, a risk score model was constructed using multivariate Cox regression analysis. We evaluated the associations between the risk score model and immune infiltration via the CIBERSORT algorithm. Moreover, we validated the signature using the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Within the ten gene signature, five rarely reported genes were further validated with quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) using an ESCC tissue cDNA microarray. Results A total of 133 up-regulated genes were identified as DEGs. Ten prognostic genes were selected based on intersection analysis of univariate COX regression analysis and PPI, and consisted of C1QA, C1QB, C1QC, CD86, C3AR1, CSF1R, ITGB2, LCP2, SPI1, and TYROBP (HR>1, p<0.05). The expression of 9 of these genes in the tumor samples were significantly higher compared to matched adjacent normal tissue based on the GEO database (p<0.05). Next, we assessed the ability of the ten-gene signature to predict the overall survival of ESCC patients, and found that the high-risk group had significantly poorer outcomes compared to the low-risk group using univariate and multivariate analyses in the TCGA and GEO cohorts (HR=2.104, 95% confidence interval:1.343-3.295, p=0.001; HR=1.6915, 95% confidence interval:1.053-2.717, p=0.0297). Additionally, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis demonstrated a relatively sensitive and specific profile for the signature (1-, 2-, 3-year AUC=0.672, 0.854, 0.81). To identify the basis for these differences in the TME, we performed correlation analyses and found a significant positive correlation with M1 and M2 macrophages and CD8+ T cells, as well as a strong correlation to M2 macrophage surface markers. A nomogram based on the risk score and select clinicopathologic characteristics was constructed to predict overall survival of ESCC patients. For validation, qRT-PCR of an ESCC patient cDNA microarray was performed, and demonstrated that C1QA, C3AR1, LCP2, SPI1, and TYROBP were up-regulated in tumor samples and predict poor prognosis. Conclusion This study established and validated a novel 10-gene signature linked with M2 macrophages and poor prognosis in ESCC patients. Importantly, we identified C1QA, C3AR1, LCP2, SPI1, and TYROBP as novel M2 macrophage-correlated survival biomarkers. These findings may identify potential targets for therapy in ESCC patients.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Jiannan Yao
- Department of Oncology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| | - Ling Duan
- Department of Oncology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| | - Xuying Huang
- Department of Oncology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| | - Jian Liu
- Department of Oncology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.,Medical Research Center, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| | - Xiaona Fan
- Department of Oncology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| | - Zeru Xiao
- Department of Oncology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| | - Rui Yan
- Department of Oncology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| | - Heshu Liu
- Department of Oncology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| | - Guangyu An
- Department of Oncology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| | - Bin Hu
- Department of Thoracic Surgery, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| | - Yang Ge
- Department of Oncology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
| |
Collapse
|
|
8
|
Lu G, Chen L, Wu S, Feng Y, Lin T. Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Relevant Therapeutic Strategy in Esophageal Cancer. DISEASE MARKERS 2020; 2020:8974793. [PMID: 32454908 PMCID: PMC7238334 DOI: 10.1155/2020/8974793] [Citation(s) in RCA: 9] [Impact Index Per Article: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [MESH Headings] [Track Full Text] [Download PDF] [Figures] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 11/16/2019] [Accepted: 03/11/2020] [Indexed: 02/07/2023]
Abstract
A growing body of evidence has indicated that behaviors of cancers are defined by not only intrinsic activities of tumor cells but also tumor-infiltrating immune cells (TIICs) in the tumor microenvironment. However, it still lacks a well-structured and comprehensive analysis of TIICs and its therapeutic value in esophageal cancer (EC). The proportions of 22 TIICs were evaluated between 150 normal tissues and 141 tumor tissues of EC by the CIBERSORT algorithm. Besides, correlation analyses between proportions of TIICs and clinicopathological characters, including age, gender, histologic grade, tumor location, histologic type, LRP1B mutation, TP53 mutation, tumor stage, lymph node stage, and TNM stage, were conducted. We constructed a risk score model to improve prognostic capacity with 5 TIICs by least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (lasso) regression analysis. The risk score = -1.86∗plasma + 2.56∗T cell follicular helper - 1.37∗monocytes - 3.64∗activated dendritic cells - 2.24∗resting mast cells (immune cells in the risk model mean the proportions of immune cell infiltration in EC). Patients in the high-risk group had significantly worse overall survival than these in the low-risk group (HR: 2.146, 95% CI: 1.243-3.705, p = 0.0061). Finally, we identified Semustine and Sirolimus as two candidate compounds for the treatment of EC based on CMap analysis. In conclusion, the proportions of TIICs may be important to the progression, prognosis, and treatment of EC.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Guangrong Lu
- Department of Gastroenterology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325000, China
| | - Liping Chen
- Department of Pharmacy, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310000, China
| | - Shengjie Wu
- Department of Pharmacy, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310000, China
| | - Yuao Feng
- College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325000, China
| | - Tiesu Lin
- Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325000, China
| |
Collapse
|
|
9
|
Recent advances in the study of regulatory T cells in gastric cancer. Int Immunopharmacol 2019; 73:560-567. [PMID: 31181438 DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.05.009] [Citation(s) in RCA: 30] [Impact Index Per Article: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Key Words] [Track Full Text] [Journal Information] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 03/13/2019] [Revised: 05/05/2019] [Accepted: 05/06/2019] [Indexed: 12/15/2022]
Abstract
Gastric cancer (GC), which features a complex pathogenesis and mechanism, remains refractory. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs), which have been implicated in the progression of gastric cancer, play an immunosuppressive role in the tumor microenvironment. However, the prognostic value of Treg infiltration is still controversial in GC patients. Recently, the association of Tregs with the clinicopathological characteristics of GC patients, the prognostic value of Tregs alone or its combination with other factors to GC patients, the role of Tregs in GC tumor microenvironment, clinical applications and Tregs-targeted therapies for GC patients have become hot issues. In this review, we are going to discuss these scientific researches which focused on these topics.
Collapse
|
|
10
|
Mimura K, Kua LF, Shimasaki N, Shiraishi K, Nakajima S, Siang LK, Shabbir A, So J, Yong WP, Kono K. Upregulation of thioredoxin-1 in activated human NK cells confers increased tolerance to oxidative stress. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2017; 66:605-613. [PMID: 28224212 PMCID: PMC11028527 DOI: 10.1007/s00262-017-1969-z] [Citation(s) in RCA: 24] [Impact Index Per Article: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Key Words] [MESH Headings] [Grants] [Track Full Text] [Journal Information] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 05/28/2016] [Accepted: 02/01/2017] [Indexed: 12/27/2022]
Abstract
Adoptive transfer of immune cells, such as T lymphocytes and NK cells, has potential to control cancer growth. However, this can be counteracted by immune escape mechanisms within the tumor microenvironment, including those mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Here, we determined the levels of anti-oxidant molecules in NK cells and their capacity to overcome ROS-induced immune suppression. We investigated the effect of H2O2 on resting NK cells, IL-2-activated NK cells and NK cells expanded by coculture with the K562 leukemia cell line genetically modified to express membrane-bound IL-15 and 4-1BB ligand (K562-mb15-41BBL). Expression of anti-oxidant and anti-apoptotic genes was evaluated by expression array, and protein levels of anti-oxidant molecules by Western blot. Activated NK cells, IL-2-activated NK cells and NK cells expanded by K562-mb15-41BBL were significantly more resistant to H2O2-induced cell death than resting NK. Thioredoxin-1 (TXN1) and peroxiredoxin-1 (PRDX1) were also up-regulated in activated NK cells. Moreover, H2O2-induced cell death after IL-2 activation was significantly induced in the presence of an anti-TXN1-neutralising antibody. Collectively, these data document that activated NK cells can resist to H2O2-induced cell death by up-regulation of TXN1.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Kousaku Mimura
- Department of Surgery, National University of Singapore, 1E Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, Singapore
- Department of Surgery, Fujikawa Hospital, Kyonan Medical Center, 340-1 Kajikazawa, Fujikawa-cho, Minamikoma-gun, Yamanashi, Japan
| | - Ley-Fang Kua
- Department of Hematology-Oncology, National University of Singapore, 1E Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, Singapore
| | - Noriko Shimasaki
- Department of Pediatrics, National University of Singapore, 1E Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, Singapore
| | - Kensuke Shiraishi
- Department of Surgery, National University of Singapore, 1E Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, Singapore
- Department of Surgery, Fujikawa Hospital, Kyonan Medical Center, 340-1 Kajikazawa, Fujikawa-cho, Minamikoma-gun, Yamanashi, Japan
| | - Shotaro Nakajima
- Cancer Science Institute of Singapore, National University of Singapore, 14 Medical Drive, #12-01, Singapore, Singapore
| | - Lim Kee Siang
- Cancer Science Institute of Singapore, National University of Singapore, 14 Medical Drive, #12-01, Singapore, Singapore
| | - Asim Shabbir
- Department of Surgery, National University of Singapore, 1E Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, Singapore
| | - Jimmy So
- Department of Surgery, National University of Singapore, 1E Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, Singapore
| | - Wei-Peng Yong
- Department of Hematology-Oncology, National University of Singapore, 1E Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, Singapore
| | - Koji Kono
- Department of Surgery, National University of Singapore, 1E Kent Ridge Road, Singapore, Singapore.
- Cancer Science Institute of Singapore, National University of Singapore, 14 Medical Drive, #12-01, Singapore, Singapore.
- Department of Organ Regulatory Surgery and Advanced Cancer Immunotherapy, Fukushima Medical University, 1 Hikarigaoka, Fukushima City, Fukushima, 960-1295, Japan.
| |
Collapse
|
|
11
|
Chen GZ, Zhu HC, Dai WS, Zeng XN, Luo JH, Sun XC. The mechanisms of radioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and current strategies in radiosensitivity. J Thorac Dis 2017; 9:849-859. [PMID: 28449496 PMCID: PMC5394057 DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2017.03.23] [Citation(s) in RCA: 61] [Impact Index Per Article: 7.6] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Key Words] [Track Full Text] [Journal Information] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Received: 10/07/2016] [Accepted: 01/19/2017] [Indexed: 12/21/2022]
Abstract
Esophageal cancer is the eighth most common cancer and the sixth leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Surgery is the primary form of treatment, but the survival is poor, especially for patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer. Radiotherapy has been a critical treatment option that may be combined with chemotherapy in patients with unresectable esophageal cancer. However, resistance to chemoradiotherapy might result in treatment failures and cancer relapse. This review will mainly focus on the possible cellular mechanisms and tumor-associated microenvironmental (TAM) factors that result in radioresistance in patients with esophageal cancer. In addition, current strategies to increase radiosensitivity, including targeted therapy and the use of radiosensitive biomarkers in clinical treatment, are discussed in this review.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Guang-Zong Chen
- Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
| | - Hong-Cheng Zhu
- Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
| | - Wang-Shu Dai
- Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
| | - Xiao-Ning Zeng
- Department of Respiratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
| | - Jin-Hua Luo
- Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
| | - Xin-Chen Sun
- Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
| |
Collapse
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Ertl HCJ. The effect of adjuvanting cancer vaccines with herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D on melanoma-driven CD8+ T cell exhaustion. JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY (BALTIMORE, MD. : 1950) 2014; 193:1836-46. [PMID: 25024391 PMCID: PMC4254702 DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302029] [Citation(s) in RCA: 18] [Impact Index Per Article: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [MESH Headings] [Grants] [Track Full Text] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Indexed: 12/22/2022]
Abstract
Two vaccines expressing CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell epitopes of melanoma-associated Ags (MAAs) by a chimpanzee-derived replication-defective AdC68 vector were compared in a mouse model of melanoma. In one vaccine, termed AdC68-gDMelapoly, the epitopes were expressed as a fusion protein within HSV-1 glycoprotein D (gD), which blocks immunoinhibitory signaling through the herpes virus entry mediator pathway. The other vaccine, termed AdC68-Melapoly, expressed only the MAA epitopes. AdC68-gDMelapoly induced more potent MAA-specific CD8(+) T cell responses especially to the subdominant MAA epitopes. Upon prophylactic vaccination, mice that developed CD8(+) T cell responses to the two vaccines that were comparable in magnitude showed equal protection against tumor challenge. When mice were first challenged with tumor cells and then vaccinated results differed. In animals with comparable CD8(+) T cell responses, the AdC68-gDMelapoly vaccine was more efficacious compared with the AdC68-Melapoly vaccine in delaying tumor growth. This effect was linked to reduced expression of 2B4, LAG-3, and programmed death-1 on tumor-infiltrating MAA-specific CD8(+) T cells elicited by the gD-adjuvanted vaccine, suggesting that CD8(+) T cells induced in presence of gD are less susceptible to tumor-driven exhaustion.
Collapse
MESH Headings
- Adjuvants, Immunologic
- Animals
- Antigens, CD/biosynthesis
- Antigens, Neoplasm/immunology
- CD4-Positive T-Lymphocytes/immunology
- CD8-Positive T-Lymphocytes/immunology
- Cancer Vaccines/immunology
- Cell Line
- Chemotherapy, Adjuvant
- Epitopes, T-Lymphocyte/immunology
- Female
- Hemagglutinins, Viral/genetics
- Hemagglutinins, Viral/immunology
- Herpesvirus 1, Human/immunology
- Lymphocyte Activation/immunology
- Melanoma/immunology
- Melanoma/prevention & control
- Melanoma/therapy
- Mice
- Mice, Inbred C57BL
- Programmed Cell Death 1 Receptor/biosynthesis
- Receptors, Immunologic/biosynthesis
- Recombinant Fusion Proteins/genetics
- Recombinant Fusion Proteins/immunology
- Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule Family
- Viral Envelope Proteins/genetics
- Viral Envelope Proteins/immunology
- Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 Protein
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Ying Zhang
- Gene Therapy and Vaccines Program, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA 19104; and
| | - Hildegund C J Ertl
- Gene Therapy and Vaccines Program, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA 19104; and Wistar Institute Vaccine Center, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104
| |
Collapse
|
|
13
|
Yang W, Jia X, Su Y, Li Q. Immunophenotypic characterization of CD45RO+ and CD45RA+ T cell subsets in peripheral blood of peripheral T cell lymphoma patients. Cell Biochem Biophys 2014; 70:993-7. [PMID: 24840225 DOI: 10.1007/s12013-014-0008-3] [Citation(s) in RCA: 2] [Impact Index Per Article: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis] [Abstract] [Track Full Text] [Journal Information] [Subscribe] [Scholar Register] [Indexed: 11/30/2022]
Abstract
To study the distribution profile of CD45RO(+) and CD45RA(+) T cells in the peripheral blood of peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL) patients and its clinical significance. 27 patients with PTCL were enrolled in this study, together with 30 healthy individuals as the control group. Flow cytometry analysis was employed to examinate the differences in the distribution of CD45RO(+) and CD45RA(+) T cells in peripheral blood between two groups. In PTCL patient's lymphnode tissues, the T cell population displayed diverse antigenic expression, with CD4(+) T cells as the major subset. No B cell-related antigen was expressed. The percentage of CD4(+)/CD8(+) and CD4(+)CD45RO(+) T cells in patients' peripheral blood were significantly lower than that in the control samples, while the percentage of CD4(+)CD45RA(+), CD8(+)CD45RA(+), and CD8(+)CD45RO(+) T cells in patients' peripheral blood were significantly higher than that in the control samples. The percentage of CD4(+)/CD8(+), CD4(+)CD45RO(+) cells in stage I/II PTCL patients' peripheral blood were significantly higher than that in the samples from patients with stage III/IV PTCL. The percentage of CD4(+)CD45RA(+), CD8(+)CD45RA(+), and CD8(+)CD45RO(+) T cells were notably lower than that in the samples from III/IV period PTCL patients. Both CD45RO(+) and CD45RA(+) T cells play important roles in the process of PTCL. The immunophenotypic profile from this study will help to develop the differential diagnosis and treatment of PTCL patients in the future, and improve the accuracy rate of diagnosis and to ameliorate the prognosis.
Collapse
Affiliation(s)
- Wenzhong Yang
- Department of Hematology Medicine East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200120, China,
| | | | | | | |
Collapse
|